
Data is an integral part of a business’s functioning, as it gives it direction and assists heavily in making decisions. Overall data can be found in many places such as websites, internal databases, and APIs, but to make use of it or simplify it for action, it needs to go through an orderly arrangement or structure which is known as data aggregation.
Data aggregation is extensively used in many industries like social media, finance, healthcare, and even eCommerce. For a company to stay afloat and function correctly, it needs to have aggregate data as it helps it keep up with competitors, find and track market trends, and even give a boost to pricing strategies. If a company does not keep up with the latest data, they are bound to fall behind and lose valuable market share.
Web scraping helps solve the issues related to collecting all the data and information automatically. It provides ease of access to all relevant data from different channels and makes use of them for business agencies to increase productivity and ease of access to customers. Before moving towards the benefits or leverages a business can have with data scraping, it is vital to understand what aggregate data is and the value it carries.
What Does It Mean to Aggregate Data?
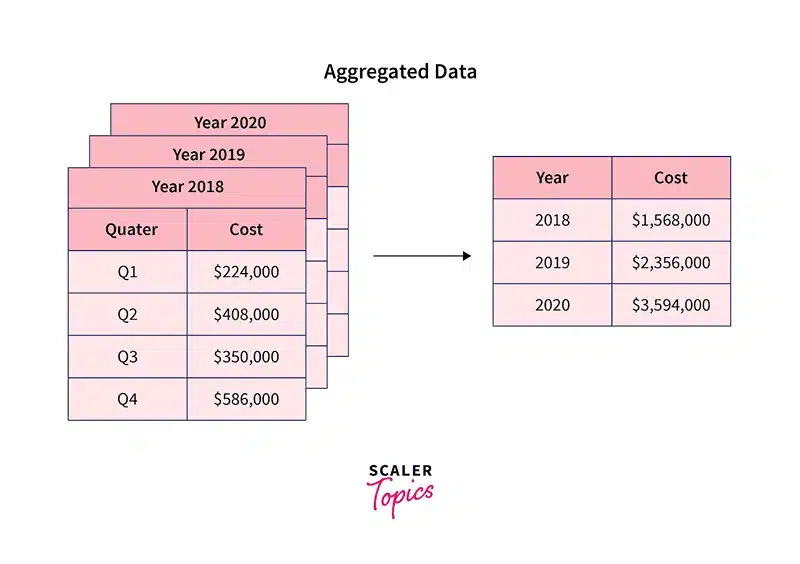
Image Source: Scaler
To aggregate data means assembling information from various sources into one dataset. When undertaking an analysis, businesses do not focus on individual data points, but rather on patterns, trends, and correlations that emerge in a larger sample.
For instance, an e-commerce company examining product prices from multiple online stores does not need individual price listings but needs an overview of the average selling prices, price variation over time, and general market trends. Likewise, a financial firm correlating stock data from multiple exchanges also needs a dataset for forecasting.
Aggregate data is different from raw data. While unsorted and inconsistent, raw data is organized and clean in comparison to aggregate data which is reliable and processed for analysis. The objective is to provide valuable insights from the copious amount of unorganized data available.
How to Aggregate Data?
Data aggregation is not merely the collection of information, rather it is the procedure of making the data usable, accurate, and valuable which follows several sequential processes. It’s usually composed of:
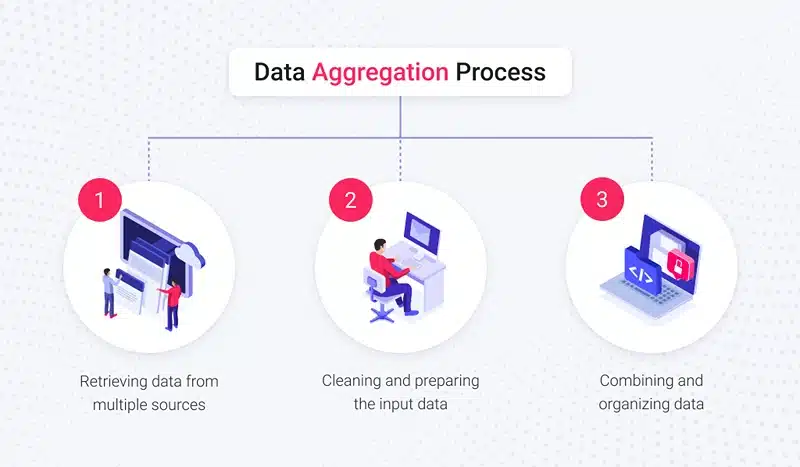
Image Source: xbsoftware
1. Data Collection
The first step in data aggregation is collecting data from various sources. These can include:
- Websites – E-commerce stores, financial news portals, real estate listings.
- APIs – Third-party data providers, stock market feeds, and social media platforms.
- Internal Databases – Customer transactions, sales records, inventory logs.
The level of effectiveness that can be achieved from aggregation will be determined by the level of trust and diversity of the sources of data.
2. Data Cleaning and Normalization
Raw data is often messy— and may contain duplicates, missing elements, or structural inconsistencies. It must be scrupulously checked, corrected, formatted in a standard manner, and uniform.
Consider a case where a business gathers pricing information from different retailers. The prices may be expressed in various forms such as $99.99, 99.99 USD, and 99,99 EUR). Every entry must be transformed into a common denominator before comparison, this is termed normalization.
3. Data Storage and Processing
Data that has been aggregated must be kept in a data warehouse, in a relational database, or in a cloud storage that is organized in a particular way. Usually, enterprises employ:
- SQL or NoSQL databases for systematically arranged data and semi-structured data.
- Cloud-based services such as AWS, Google BigQuery, and Azure for flexibility and expansion.
- Big Data frameworks like Apache Hadoop or Spark for large-scale processing.
4. Data Analysis and Reporting
After aggregating data businesses can conduct an analysis using:
- Business Intelligence (BI) platforms such as Tableau, Power BI, or Looker.
- AI and Machine Learning models for predictive analytics.
- Statistical methods to detect trends and patterns.
What are the Types of Data Aggregation?
With various sectors having diverse approaches to data aggregation, the key categories are outlined below:
1. Temporal Aggregation
As the name suggests, temporal aggregation encompasses grouping data by time intervals, such as hours, days, weeks, and even months. A hypothetical example is an online streaming platform that aggregates viewership data to determine peak days of the week for online engagement.
Businesses capitalize on the advantages of temporal aggregation to uncover seasonal shifts alongside other enduring trends in consumer activity.
2. Spatial Aggregation
Spatial aggregation is a geographical term. It refers to grouping data by geographical areas like town, city, region, or even country. It is very beneficial for companies that have a presence in numerous locations. For example, a ride-hailing business could look at the demand for rides in various cities to better allocate drivers and enhance service coverage in high-demand areas.
3. Categorical Aggregation
In this type of aggregation, data is grouped with respect to specific predefined criteria like customer age, gender, or even industry segments. An example of categorical data aggregation is that conducted by an e-commerce platform, which aggregates data from sales of different products such as electronics, fashion, and groceries to determine the most profitable sector.
4. Numerical Aggregation
Statistical methods are employed on numerical data sets in order to achieve totals, averages, or percentiles in the process known as numerical aggregation. When analyzing the volume and volatility of stocks in the market, for example, a financial analyst may look at aggregating the movement of stock prices.
Why Do Businesses Need to Aggregate Data?
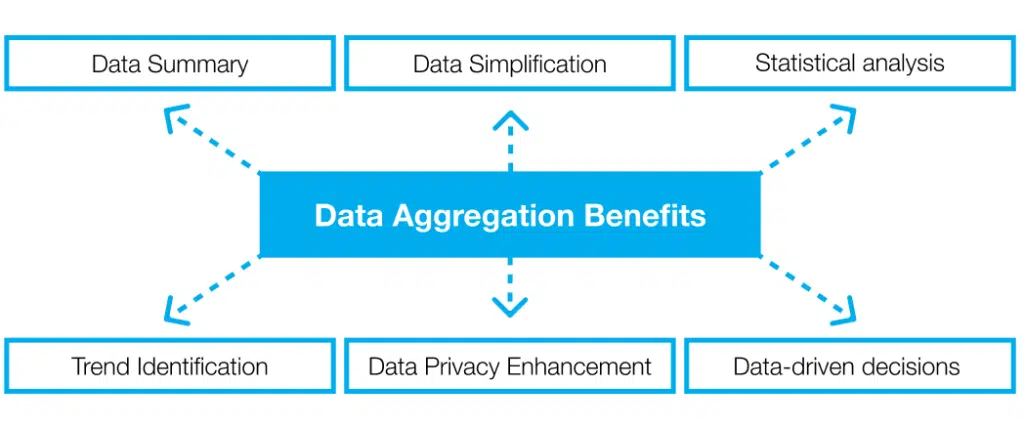
Image Source: onaudience
Data aggregation is important for any organization that derives significant value from data analytics. Here is how it benefits a business:
1. Enhancing Decision-Making
Aggregate data is useful for businesses looking to spot performance anomalies and adjust appropriately. Retailers, for example, aggregate customer transactions to evaluate which products are selling and which require advertising.
2. Gaining Competitive Intelligence
By aggregating data from various competitors, businesses can evaluate pricing, perception, and placement. This allows them to stay relevant in highly competitive markets.
3. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Finance and healthcare industries are some of the sectors where compliance-driven data aggregation is required. For instance, banks aggregate transaction data for fraud detection and ensure anti-money laundering compliance.
4. Improving Customer Experiences
The personalization of advertising and marketing campaigns is achievable by aggregating consumer interactions and activities on different channels. An airline, for example, could target customers with travel deals based on their booking data.
Use Cases of Data Aggregation
1. E-commerce: Optimizing Pricing, Inventory, and Consumer Insights
During retail operations e-commerce businesses function within a tight margin control environment with changes in pricing or product availability being critical to success. By collecting and analyzing data from websites, customer reviews, and sales reports, retailers can:
- Implement dynamic pricing – E-commerce platforms aggregate data on prices from competitors to adjust their own prices in real time, ensuring they remain competitive without sacrificing profit margins.
- Predict demand fluctuations – Businesses can maintain optimal inventory levels by minimizing stockouts and overstocking by analyzing historical sales data, seasonal trends, and customer search behavior.
- Enhance customer personalization – Enhanced data from user behavior capturing browsing or purchasing, enables businesses to personalize product recommendations yielding increased sales and enhanced customer satisfaction.
2. Finance and Investment: Market Intelligence and Risk Assessment
Businesses and Financial institutions investment rely heavily on large-scale data e.g. competitor pricing data to analyze benchmark spend volumes during market trends, conduct risk assessment, and make informed decisions. Some important applications include:
- Stock market predictions – Aggregating historical stock price and trading volume data along with other global economic indicators enables analysts to design predictive models for advanced investment strategies.
- Fraud detection – Banks use aggregated transaction data to monitor and detect abnormal spending patterns which could indicate fraudulent activities in real time.
- Risk management – Insurance companies and hedge funds collect and aggregate data for assessing the volatility of the markets to optimize their portfolios.
3. Healthcare: Improving Patient Outcomes and Medical Research
The volume of data associated with patient records, clinical trials, wearable devices, and medical research is enormous within the healthcare sector. Aggregating this data enables:
- Personalized treatment plans – With the help of aggregate data concerning patients’ medical history and treated cases, hospitals tailor their approach to develop specific treatment plans, thus offering personalized medicine.
- Disease outbreak tracking – Aggregated health data from diverse channels such as hospitals, pharmacies, and online health discussions can be aggregated to assist public health institutions in monitoring, predicting and controlling outbreaks of diseases.
- Medical research acceleration – The aggregation of research papers, experimental results, and genomic data makes it possible for scientists to find new patterns leading to drug development and treatment innovations.
4. Social Media and Brand Monitoring: Sentiment Analysis and Trend Detection
The vast amount of user-generated content on social media platforms has made the need for social media monitoring critical for brands. Business entities can benefit greatly from the integration of data from social media, blogs, and news publications as they can:
- Track brand sentiment – Through the implementation of AI, customer reviews, comments on social media platforms, and discussion forums can be analyzed to gauge public perception.
- Identify emerging trends – Businesses evaluate conversations to determine topics that are going viral, helping them better understand consumer interests for effective marketing.
- Competitor benchmarking – Businesses study the aggregated engagement statistics of the competitors to improve their own social media strategies.
5. Supply Chain and Logistics: Enhancing Efficiency and Reducing Costs
Supply chain management relies on aggregated data from suppliers, transportation networks, and warehouses to optimize logistics and reduce operational costs. Some critical use cases include:
- Route optimization – Logistic businesses analyze aggregated traffic conditions, meteorological data, and delivery timelines to establish the best and most fuel-efficient routes for deliveries.
- Demand forecasting – Aggregated sales and inventory data enable businesses to foresee potential disruptions in the supply chains, leading to altered procurement plans.
- Supplier performance analysis – Companies aggregate data on supplier delivery times, product quality, and pricing to evaluate and negotiate better contracts.
6. Recruitment and HR Analytics: Workforce Planning and Talent Acquisition
Aggregating job market data helps businesses improve their hiring strategies by analyzing employment trends, salary benchmarks, and in-demand skills. Key applications include:
- Competitive salary analysis – HR teams use aggregated job listing data to set competitive salaries based on industry standards and location-based trends.
- Talent sourcing optimization – Recruitment platforms aggregate candidate profiles from multiple job boards to match employers with suitable candidates more efficiently.
- Workforce retention strategies- HR attains feedback from employees and uses that data to shed light on workplace concerns and enhance retention through satisfaction policies.
7. Real Estate and PropTech: Property Valuation and Market Analysis
The real estate industry relies heavily on aggregate data to evaluate investment risks, property values, and market trends. Data aggregation within the real estate industry includes:
- Property price analysis – The data aggregation of sales and rental listings, along with neighborhood statistics aids buyers and investors in determining the value of a property.
- Urban development planning – Aggregated demographic and economic data is used by governments and developers to aid in planning new infrastructure projects.
- Risk assessment for investments – Real estate organizations evaluate aggregated economic parameters, mortgage rates, and demand to predict shits in the market.
Manual vs. Automatic Data Aggregation
Traditionally, data aggregation was performed manually, but automation has revolutionized the process. Here’s a comparison:
| Aspect | Manual Data Aggregation | Automatic Data Aggregation |
| Speed | Slow and time-consuming | Fast and efficient |
| Accuracy | Prone to human errors | High accuracy, minimal errors |
| Scalability | Limited to small datasets | Scales easily to large datasets |
| Cost | High due to labor costs | Lower in the long run |
| Flexibility | Difficult to adapt to changes | Easily adaptable with AI/ML tools |
How Businesses Leverage Web Scraping for Large-Scale Data Aggregation
With information being distributed on millions of web pages, scraping websites has become one of the most efficient means to collect and aggregate useful data at a large-scale. Automated methods of extracting structured data from websites such as web scraping simplifies the process.
- Extracting Market Intelligence – Businesses scrape and aggregate data from competitor websites, news portals, and financial reports. This assists organizations in pricing strategies and determining trends, gaining an advantage over their competitors. Knowing industry preferences is also important.
- Monitoring Online Reviews and Sentiment – Businesses scrape the internet for product reviews, social media comments, and forum discussions in order to analyze customer sentiment. Therefore allowing brands to satisfy customers and deal with negative feedback in advance.
- Tracking Price Fluctuations – Sellers on ecommerce platforms aggregate data from multiple sellers in order to optimize pricing strategies and prevent losing market share due to price variations.
- Collecting Real-Time Financial Data – Investment firms and fintech companies scrape stock market data such as cryptocurrency prices and other economic indicators to create predictive trading models.
- Aggregating Job Market Trends – Businesses scrape job postings from various recruitment platforms in order to analyze hiring trends, salary benchmarking, and demand for certain skills.
Benefits of Web Scraping for Large-Scale Data Aggregation
Web scraping has changed the way businesses aggregate data and comes with a lot of benefits including:
- Scalability – Traditional techniques are not capable of handling the amount of data available online. With web scraping, businesses can extract and process enormous amounts of data easily.
- Real-Time Insights – Unlike static reports, web scraping will always be up to date, therefore providing businesses with timely information that will aid in making faster decisions.
- Cost Savings – Aggregating data through web scraping eliminates the need for third-party data providers. Manual data entry that is often done by employees also gets reduced through automation
- Data-Driven Strategies – Having precise and complete data allows businesses to improve marketing, sales, and operation strategies.
Challenges Businesses Face in Data Aggregation
While data aggregation is crucial, businesses often encounter challenges in the process:
- Data Quality Issues – Inconsistent or incomplete data can lead to misleading insights. Companies must invest in data validation and cleaning mechanisms.
- Legal and Ethical Concerns – Scraping publicly available data is common, but some websites impose restrictions. Businesses need to ensure compliance with legal guidelines.
- Infrastructure and Storage – These systems come with high maintenance costs. Businesses must have advanced storage and computing frameworks to effectively manage large datasets, referred to as big data.
- Data Integration – There are many issues related to the integration of data and dissimilar formats from numerous sources. Companies need to implement correct ETL methods for integration.
Why Choose PromptCloud for Large-Scale Data Aggregation
Web scraping has become an essential tool for businesses that rely on large-scale data aggregation. However, setting up and maintaining a robust scraping infrastructure requires expertise, resources, and compliance with ethical data collection standards.
At PromptCloud, we specialize in high-quality, scalable web scraping solutions tailored to your business needs. Whether you need market intelligence, competitor analysis, or sentiment tracking, we help you collect and aggregate data efficiently while ensuring compliance with regulations.If you’re looking for a reliable data aggregation partner, get in touch with us today and unlock the power of large-scale data insights for your business.


















