
What is a Web Crawler?
A web crawler, also known as a spider or bot, is a specialized software program designed to browse the internet systematically. It collects data from websites by indexing pages based on keywords and content. This data is then used for various purposes such as search engine indexing, data analysis, and market research.
Web crawlers navigate through links on web pages, fetching data and downloading it to a database for further processing. They follow a specific set of rules called the “robots.txt” directive to determine which pages can be crawled and indexed, ensuring they respect the website owner’s preferences.
To help you navigate the world of web crawlers, we’ve compiled a comprehensive web crawler list that highlights the top performers in 2025. This guide will explore the importance of web crawlers, their impact on the digital ecosystem, and key criteria for selecting the best crawler to meet your needs.
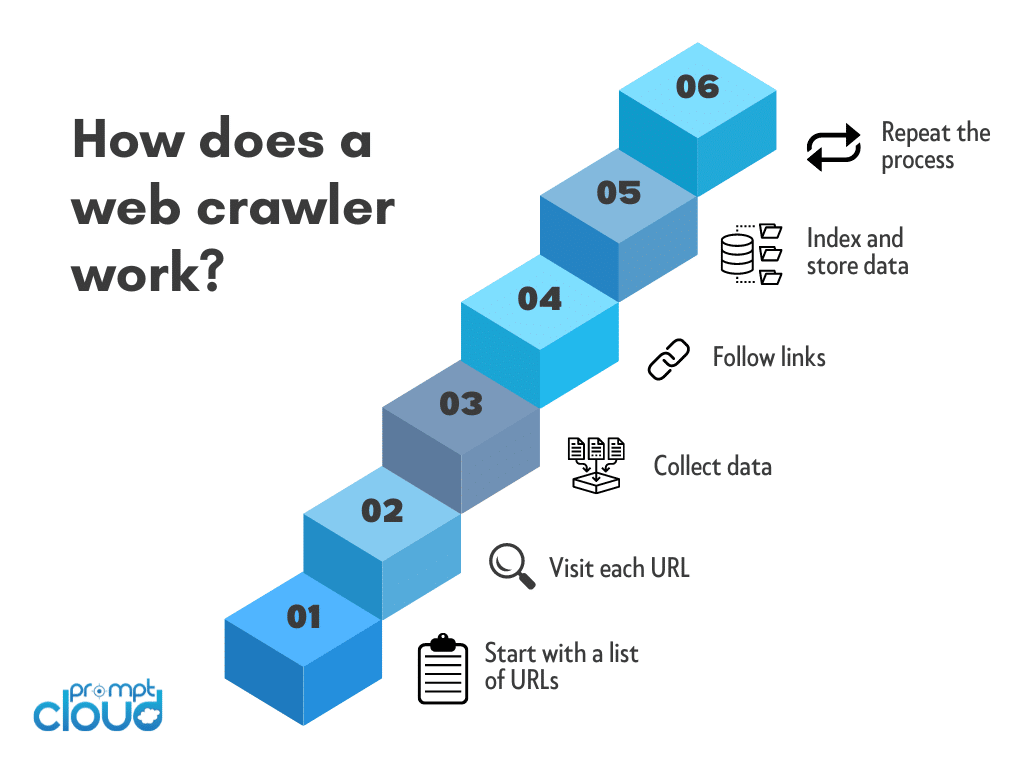
What is the Importance of Web Crawlers?
In 2025, the significance of web crawlers has augmented due to the exponential growth of digital content and e-commerce platforms. Web crawlers enable search engines to index massive volumes of data, ensuring users receive accurate and timely search results. Additionally, web crawlers facilitate competitive analysis by scanning websites for price comparisons, market trends, and customer feedback.
Data-driven insights derived from web crawlers support businesses in optimizing their strategies and enhancing user experience. Furthermore, web crawlers aid in monitoring website health by identifying broken links, duplicates, and other SEO issues, thereby ensuring optimal functionality and improved ranking.
Significance of Web Crawlers in the Digital Ecosystem
Web crawlers play a crucial role in the digital ecosystem by systematically navigating and indexing the vast content across the internet. They enable search engines to deliver relevant results, assist businesses in tracking competitors, and facilitate data mining for market insights. Moreover, web crawlers support cybersecurity by detecting anomalies and potential threats.
They are also employed in academic research to gather data, in e-commerce to aggregate pricing information, and in social media monitoring to analyze trends. Overall, web crawlers enhance the accessibility, security, and intelligence of the digital landscape.
How to Choose the Best Web Crawler in 2025?
Choosing a web crawler from the top 5 in 2025 crawler list demands a focus on specific criteria to meet diverse needs. Scalability is crucial for handling large datasets efficiently. Customization options ensure that the crawler can adapt to unique requirements.
High accuracy is vital to minimize errors in data collection. The crawler should also be compliant with the latest web standards and guidelines to avoid legal issues. Performance metrics such as speed and resource usage are essential for maximizing efficiency. Lastly, support and documentation are indispensable for troubleshooting and optimum utilization.
1. Googlebot: The Ubiquitous Search Giant

Image Source: Seobility
Googlebot is the web crawling bot used by Google to index web pages. As one of the most advanced and ubiquitous crawlers, it plays a critical role in how web content gets discovered and ranked. Googlebot’s sophisticated algorithms and adaptability make it an indispensable tool for accurate and timely web indexing.
- Crawling Frequency: Googlebot crawls websites constantly, keeping search results up to date with the latest content changes.
- Mobile-First Indexing: Prioritizes mobile content to align with Google’s mobile-first indexing approach.
- Desktop Crawler: Also maintains a desktop version to cover all types of web content.
- Respect for Robots.txt: Adheres to the instructions specified in a website’s robots.txt file.
- JavaScript Rendering: Capable of rendering JavaScript, ensuring more dynamic content gets indexed correctly.
2. Bingbot: Microsoft’s Answer to Google
2nd on our crawler list is Bingbot, Microsoft’s web crawler used to index web pages for their Bing search engine. Launched in 2010, it offers robust crawling capabilities. Microsoft continuously updates Bingbot to enhance its efficiency and indexing performance, positioning it as a formidable contender to Googlebot in the search engine sector.
- Crawling Efficiency: Bingbot navigates vast web landscapes, ensuring Bing’s search results are comprehensive.
- Respectful Crawling: Adheres to the site’s robots.txt, allowing respectful and efficient crawling.
- User-Agent Identification: Identified by the User-Agent string “Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; bingbot/2.0; +http://www.bing.com/bingbot.htm)”.
- Technology Integration: Utilizes machine learning and AI integrations to improve search index accuracy.
3. Yandex Bot: A Rising Star in Web Crawling
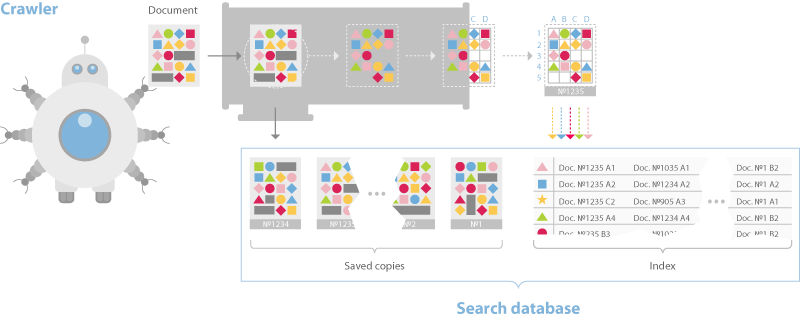
Image Source: Yandex
Yandex Bot is a powerful web crawler developed by the Russian search engine Yandex. Its capabilities in indexing and data extraction are rapidly gaining attention globally.
- Efficiency: Yandex Bot is known for its efficient and systematic crawling, ensuring comprehensive web coverage.
- Advanced Algorithms: Employs sophisticated AI and machine learning algorithms for improved relevance and accuracy.
- Regional Focus: Particularly excels in indexing Russian and Cyrillic content, but is expanding its global reach.
- Respectful Crawling: Adheres strictly to robots.txt and avoids overloading servers.
- Real-time Updates: Provides up-to-date indexing, important for news and e-commerce sites.
4. PromptCloud: Custom Web Crawling Service Provider
PromptCloud is one of the web crawlers in this crawler list that offers custom web crawling and data extraction services, catering to businesses seeking precise web data.
Key Features
- Customizable Solutions: Adapts to various data requirements.
- Real-Time Data Access: Provides fresh, frequently updated datasets.
- Structured Data Delivery: Ensures clean, ready-to-use data formats.
- High Scalability: Handles significant data volumes effortlessly.
Applications
- Market Research: Supplies competitive analysis data.
- E-commerce: Collects product details and pricing information.
- Job Market Insights: Aggregates job listings and company reviews.
Benefits
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for internal resources.
- Quality Assurance: Delivers reliable data outputs.
- Rapid Deployment: Enables swift integration with existing systems.
5. AhrefsBot: The SEO Specialist’s Best Friend
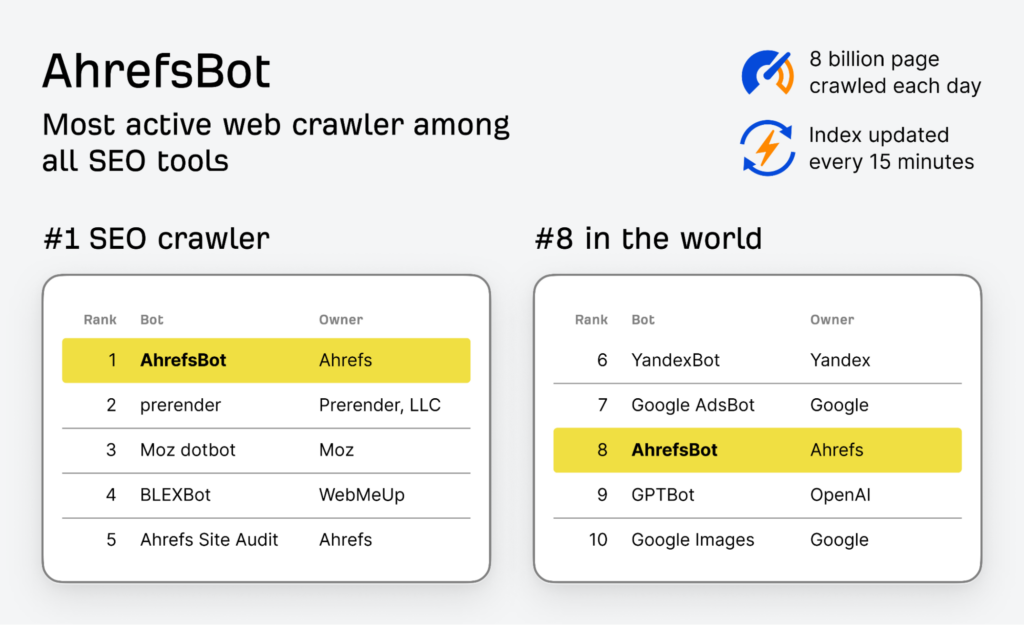
Image Source: AHREFS
AhrefsBot stands out in the SEO world for its efficiency and accuracy in web crawling. It is designed to collect data crucial for search engine optimization. AhrefsBot scans websites to gather information about backlinks, keywords, and other SEO metrics.
Key Features:
- High Crawl Speed: Swiftly navigates through large websites.
- Real-Time Data: Provides up-to-date information on backlinks and keywords.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Generates detailed analyses of site performance.
What Makes These Web Crawlers Exceptional?
- Speed and Efficiency
- High-speed data processing with algorithms to ensure minimal resource usage.
- Optimized for faster network crawling with reduced latency.
- Scalability
- Capable of handling extensive data across multiple servers.
- Supports horizontal scaling for enhanced performance.
- Customizability
- Offers extensive API support for custom scripts and configurations.
- Adaptive to varied data structures and formats.
- Accuracy
- Incorporates advanced error-checking mechanisms.
- Ensures accurate and reliable data extraction.
- Security
- Features robust security protocols to prevent data breaches.
- Provides secure data transfer and storage options.
- Compliance
- Adheres to web scraping laws and regulations.
- Integrates features to respect the robots.txt guidelines.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of web crawlers requires expertise, and PromptCloud offers unparalleled solutions. Companies looking to leverage efficient data scraping should consider PromptCloud’s advanced capabilities. Our platform ensures real-time data extraction, exceptional reliability, and adherence to legal standards.
Businesses can expect customized solutions tailored to their specific needs, enabling them to make data-driven decisions with confidence. Explore PromptCloud today to streamline your web crawling efforts and stay ahead of the competition. Contact us and discover how our services can transform your data strategy and stand out in this web crawler list.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a crawler?
A crawler, also known as a web crawler or spider, is a type of software or bot designed to automatically browse the internet, systematically scanning and indexing web pages. Crawlers navigate the web by following links from one page to another, much like a human user would, but on a much larger scale and at a much faster pace.
The primary purpose of a crawler is to collect data from websites, which can then be used for various purposes, such as building search engine indexes, conducting web scraping, or gathering data for analysis. For example, search engines like Google use crawlers to index the content of web pages so that they can be retrieved quickly in response to user queries.
In the context of data extraction and web scraping, crawlers are often employed to automatically gather large amounts of data from multiple websites, following links to access relevant pages, and extracting the desired information. These tools can be customized to focus on specific types of data, making them a powerful tool for businesses that need to collect and analyze web-based information efficiently.
At PromptCloud, we leverage advanced crawling techniques to ensure that our clients get accurate, up-to-date data, even from websites with complex structures. Whether you need data for market research, price monitoring, or competitive analysis, our crawlers can help you gather the information you need seamlessly and efficiently.
How many types of crawlers are there?
There are several types of crawlers, each designed for specific purposes and functionalities. Here are the main types of crawlers:
1. Search Engine Crawlers
- Purpose: Indexing web pages for search engines.
- Description: These crawlers, also known as spiders or bots, are used by search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo to scan and index content from across the web. They follow links on web pages to discover new or updated content and add it to the search engine’s database.
- Example: Googlebot.
2. Web Scraping Crawlers
- Purpose: Extracting specific data from websites.
- Description: Web scraping crawlers are designed to gather targeted data from web pages. These crawlers can be customized to extract specific types of information, such as product prices, customer reviews, or contact information, and are often used in market research, price monitoring, and data aggregation.
- Example: Custom web scrapers built with tools like Scrapy or BeautifulSoup.
3. Focused Crawlers
- Purpose: Gathering information on specific topics or domains.
- Description: Focused crawlers, also known as topical crawlers, are programmed to search the web for information related to a specific topic or set of keywords. Unlike general search engine crawlers, these crawlers are designed to ignore irrelevant content and focus only on web pages that match the defined criteria.
- Example: A crawler designed to collect articles related to a specific industry or technology.
4. Incremental Crawlers
- Purpose: Updating existing data with new or changed content.
- Description: Incremental crawlers are designed to revisit web pages that have already been crawled to detect and capture any changes or updates. This type of crawler is essential for keeping a database or index up-to-date with the latest content without re-crawling the entire web.
- Example: A news aggregator that updates its content based on the latest articles.
5. Deep Web Crawlers
- Purpose: Accessing content not indexed by standard search engines.
- Description: Deep web crawlers are designed to access content that is typically hidden from regular search engines, such as databases, password-protected sites, and dynamic content generated by user queries. These crawlers are more sophisticated and often require specific permissions or advanced techniques to access non-public data.
- Example: Crawlers used to gather data from academic databases or subscription-based services.
6. Distributed Crawlers
- Purpose: Efficiently crawling large-scale web data across multiple systems.
- Description: Distributed crawlers divide the task of crawling across multiple machines or servers to increase efficiency and speed. This type of crawler is used when the data to be collected is vast, and a single machine cannot handle the load efficiently.
- Example: Large-scale web scraping projects that require parallel processing.
7. Polite Crawlers
Example: A web scraper programmed with rate limiting to prevent excessive load on the target site.
Purpose: Respecting website load and preventing server overload.
Description: Polite crawlers are designed to be respectful of the websites they crawl by limiting the number of requests they make in a given period. They follow the site’s robots.txt file and use delays between requests to avoid overwhelming the server.
What is a crawler in social media?
A crawler in social media, often referred to as a social media crawler, is a specialized software tool designed to automatically browse and extract data from social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, and others. These crawlers are used to gather a wide range of information from social media sites, including posts, comments, likes, shares, follower counts, and user profiles. Here’s a more detailed explanation:
Purpose of Social Media Crawlers
Social media crawlers are typically used for several key purposes:
- Sentiment Analysis: Collecting and analyzing user comments, posts, and reviews to gauge public sentiment towards a brand, product, or topic.
- Trend Monitoring: Identifying and tracking trending topics, hashtags, and discussions to stay updated with current events or popular content.
- Competitor Analysis: Gathering data on competitors’ social media activity, including follower growth, engagement rates, and content strategies.
- Influencer Identification: Identifying and analyzing the influence of key individuals or accounts within a specific niche or industry.
- Content Aggregation: Collecting and curating content from multiple social media platforms for reposting, analysis, or research purposes.
- Market Research: Understanding consumer behavior, preferences, and feedback through analysis of social media interactions.
How Social Media Crawlers Work
Social media crawlers operate by navigating through social media platforms, following links between profiles, posts, and other content, and extracting relevant data. Depending on the crawler’s configuration, it can:
Respect Rate Limits and Policies: Social media platforms often have rate limits (limits on the number of requests that can be made in a given time frame) and strict policies on data access. Ethical crawlers are designed to respect these limitations to avoid being blocked or causing disruptions to the platform.
Scrape Public Data: Extract data that is publicly accessible, such as public profiles, posts, comments, likes, and shares.
Interact with APIs: Many social media platforms offer APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow for more structured and legitimate access to data. Crawlers can interact with these APIs to gather data in a more controlled and ethical manner.
Handle Dynamic Content: Social media platforms often use dynamic content (content that loads as you scroll or interact with the page). Advanced crawlers can handle this by simulating user interactions, like scrolling or clicking, to access all available data.
How do I find a crawler?
Finding a crawler depends on what you need it for, whether it’s for web scraping, social media monitoring, or another purpose. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to find a crawler that suits your needs:
1. Define Your Requirements
- Purpose: Determine what you need the crawler for. Are you looking to scrape data from websites, monitor social media, or index a specific type of content?
- Technical Skills: Assess your technical skills. Do you need a no-code solution, or are you comfortable with coding?
- Scale: Consider the scale of your project. Do you need to crawl a few pages or thousands of websites?
- Data Type: Identify the type of data you need to collect (e.g., text, images, structured data like tables).
2. Search for Crawler Tools
- General Web Crawlers: For web scraping and crawling general websites, you can search for tools like Scrapy (Python), BeautifulSoup (Python), Octoparse, or ParseHub. These are some of the most popular options.
- Social Media Crawlers: For social media data extraction, you might look for tools like Social Media APIs (Twitter API, Facebook Graph API), NodeXL (for network analysis), or third-party tools like Brandwatch or Hootsuite Insights.
- Search Engine Crawlers: If you’re looking for a crawler to build or manage a search engine, you might consider tools like Apache Nutch or Heritrix.
- Custom Crawlers: If you need a highly customized crawler, consider hiring a developer to build one tailored to your specific needs using programming languages like Python, Java, or Node.js.
3. Explore Online Marketplaces and Repositories
- GitHub: Search for open-source crawlers on GitHub. There are many pre-built crawlers and frameworks that you can use or modify to fit your needs.
- Software Marketplaces: Websites like SourceForge or CodeCanyon may have crawler tools that you can purchase or download.
4. Read Reviews and Documentation
- Before selecting a crawler, read user reviews, documentation, and tutorials to ensure the tool meets your requirements. Look for detailed documentation to help you understand how to set up and use the crawler effectively.
5. Test the Crawler
- Once you’ve found a potential crawler, test it on a small scale to ensure it works as expected. Check for factors like ease of use, accuracy, speed, and how well it handles the type of data you need.
6. Consider Legal and Ethical Aspects
- Make sure that the crawler you choose complies with the terms of service of the websites you plan to crawl. Also, ensure that it respects data privacy regulations and ethical guidelines.
7. Join Communities and Forums
- Engage with online communities such as Stack Overflow, Reddit, or specialized forums where you can ask for recommendations and advice on the best crawlers for your needs.
8. Consult a Professional
If your crawling needs are complex or you’re unsure which tool to choose, consider consulting a professional or hiring a developer with expertise in web crawling and data extraction.
What is an example of crawling?
An example of crawling is the process used by search engines like Google to discover and index new or updated content on the internet. Here’s how it typically works:
Example: Googlebot Crawling a Website
- Initiation:
- Googlebot, Google’s web crawler, starts by visiting a known URL. This URL could be from a previous crawl, a link found on another website, or a newly submitted URL through Google Search Console.
- Navigating Links:
- Once Googlebot accesses the initial webpage, it scans the HTML code for hyperlinks that point to other pages within the same domain or external domains. For example, if it starts at the homepage of a website, it might find links to other pages like “About Us,” “Products,” “Blog,” etc.
- Following Links:
- Googlebot follows these links to discover new pages. As it visits each page, it continues to follow any additional links it finds, allowing it to explore the entire website or even move to other websites.
- Content Extraction:
- During the crawl, Googlebot extracts content from the pages it visits. This includes text, images, metadata, and other relevant information. It also looks for important signals like the presence of keywords, the structure of the content, and the relevance of the material to users.
- Indexing:
- The collected data is then processed and stored in Google’s index, which is a massive database of web content. When a user performs a search, Google refers to this index to find the most relevant results.
- Handling Updates:
- Googlebot periodically revisits the website to check for any changes or new content. For example, if the website owner adds a new blog post, Googlebot will eventually crawl the new content and update the index accordingly.
Practical Application:
Imagine you own an online store that sells shoes. To ensure your products appear in Google search results, Googlebot needs to crawl your website. As Googlebot visits your site, it will follow links to different product pages, extract details like product descriptions, prices, and images, and then index this information so that it can be displayed in search results when users search for shoes.
What is the meaning of data crawling?
Data crawling refers to the automated process of systematically browsing and extracting data from websites or other online sources. A data crawler, often called a web crawler or spider, is a software program or script that navigates through web pages by following links, gathering the desired data, and storing it for analysis or further use.
Key Aspects of Data Crawling:
Ethical data crawling respects the rules set by websites, often defined in the robots.txt file. This file indicates which parts of the site can be crawled and which should be avoided. Additionally, responsible crawlers include rate limiting to avoid overwhelming a website’s server.
Systematic Browsing:
Data crawling involves systematically visiting web pages, starting from a specific URL (such as a homepage) and then following links to other pages within the same site or across different sites. This allows the crawler to explore and collect data from a wide range of sources.
Data Extraction:
The primary goal of data crawling is to extract specific types of information from web pages. This could include text, images, metadata, links, or any other content available on the page. The extracted data is usually stored in a structured format, such as a database, spreadsheet, or JSON file.
Automation:
Data crawling is an automated process, meaning that it operates without manual intervention. Crawlers can be configured to run at specific intervals, continuously monitoring and collecting data from the web.
Use Cases:
Data crawling is used in various applications, including:
Search Engines: Crawlers index web pages to make them searchable by users.
Market Research: Businesses use crawlers to gather competitive intelligence, monitor prices, and analyze consumer behavior.
Content Aggregation: News sites and blogs collect content from multiple sources for curation.
Data Mining: Researchers collect large datasets for analysis in fields like social science, finance, and more.
Handling Dynamic Content:
Some advanced crawlers are capable of handling dynamic content, such as pages that load additional data via JavaScript or AJAX. These crawlers can simulate user interactions like scrolling or clicking to access and extract this data.
Respecting Website Protocols:
Ethical data crawling respects the rules set by websites, often defined in the robots.txt file. This file indicates which parts of the site can be crawled and which should be avoided. Additionally, responsible crawlers include rate limiting to avoid overwhelming a website’s server.
How does SEO crawling work?
SEO crawling is a critical process in search engine optimization (SEO) that involves search engine bots, or crawlers, systematically scanning a website’s content to understand its structure, index its pages, and determine its relevance for search queries. Here’s how SEO crawling works:
1. Initiation of Crawling
- Starting Point: SEO crawling typically begins when a search engine’s crawler, such as Googlebot, accesses a website. This can happen when the crawler discovers the site through links from other sites, from a sitemap submission, or from previous crawling sessions.
- URL Discovery: Crawlers identify new URLs by following links within the website (internal links) or from external websites (backlinks). They prioritize which pages to crawl based on factors like page authority, freshness of content, and the website’s overall structure.
2. Following Links
- Internal Links: Crawlers follow internal links within the website to navigate through different pages. This is why having a well-structured internal linking system is important for SEO—it helps crawlers discover all the content on your site.
- External Links: Crawlers also follow external links, which can help them discover new sites or validate the relevance and authority of your content.
3. Content Analysis
- HTML and Meta Tags: Crawlers analyze the HTML structure of the page, including important SEO elements like title tags, meta descriptions, headers (H1, H2, etc.), and alt attributes for images. These elements provide information about the content and relevance of the page.
- Text Content: Crawlers read and index the actual text on the page to understand its topic and relevance to potential search queries. Keyword usage, content depth, and overall quality play a crucial role in how the content is perceived by search engines.
- Structured Data: If the site uses structured data (like Schema.org), crawlers can better understand specific content types, such as reviews, products, or events, which can enhance search engine listings (rich snippets).
4. Handling Different Types of Content
- Dynamic Content: SEO crawlers can handle dynamic content that loads via JavaScript or AJAX. Advanced crawlers simulate user interactions, like scrolling or clicking, to ensure all content is indexed.
- Multimedia: While crawlers primarily focus on text, they also identify multimedia elements like images and videos. Optimizing these elements with appropriate alt tags and descriptions helps crawlers understand and index them correctly.
5. Respecting Robots.txt and Meta Robots
- robots.txt File: This file instructs crawlers on which parts of the website should or should not be crawled. For example, you might block crawlers from accessing admin pages or duplicate content.
- Meta Robots Tag: This HTML tag is used on individual pages to control how and whether a page should be indexed by the search engine and whether the links on that page should be followed.
6. Indexing
- Content Storage: Once the crawling process is complete, the data collected is stored in the search engine’s index. This index is a massive database where the search engine stores all the information about the web pages it has crawled.
- Indexing Criteria: Not all crawled pages are indexed. The decision to index a page depends on its content quality, relevance, user experience factors (like page speed and mobile-friendliness), and compliance with search engine guidelines.
7. Revisiting and Re-crawling
- Periodic Crawling: Search engines periodically re-crawl websites to detect new content or updates. Pages with high authority or frequent updates might be crawled more often.
- Sitemaps: Submitting an XML sitemap to search engines can help ensure all pages on your site are discovered and crawled, even those not easily reachable through internal links.
8. Handling SEO Errors
Crawl Errors: Crawlers may encounter issues like broken links, server errors, or blocked pages. Tools like Google Search Console help webmasters identify and fix these crawl errors, improving the site’s SEO performance.
Are crawlers legal?
The legality of crawlers, also known as web crawlers or spiders, depends on how they are used and the specific circumstances surrounding their deployment. Here are some key points to consider:
1. General Legality
- Crawling as a Technique: The act of crawling itself—where a program automatically navigates websites and extracts data—is not inherently illegal. In fact, search engines like Google and Bing use crawlers legally to index web pages for search purposes.
- Common Use Cases: Crawlers are commonly used for legitimate purposes such as search engine indexing, monitoring website uptime, and aggregating publicly available information.
2. Website Terms of Service
- Terms of Service Violations: Many websites include clauses in their terms of service that restrict or prohibit automated crawling or data extraction. Violating these terms can lead to legal action, such as being banned from the site or sued for breach of contract.
- robots.txt: Websites often use a
robots.txtfile to specify which parts of the site should not be crawled. While this file is a standard way of communicating with crawlers, it is not legally binding. However, ignoringrobots.txtinstructions could contribute to a claim of unauthorized access or bad faith.
3. Copyright and Intellectual Property
- Content Scraping: Crawling that involves copying or redistributing copyrighted content, especially for commercial purposes, can infringe on intellectual property rights. This is especially true if the content is used without permission and in a way that could harm the rights holder’s business.
- Fair Use: In some cases, limited scraping for purposes like research or commentary might be protected under fair use doctrines, but this is highly context-dependent and often requires legal interpretation.
4. Data Privacy Regulations
- Personal Data: If a crawler collects personal data, such as names, emails, or other identifiable information, it must comply with data privacy laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). These laws often require clear consent from the data subjects before their data can be collected and processed.
- Compliance: Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines and legal action.
5. Unauthorized Access
- Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA): In the United States, unauthorized access to computer systems, including websites, is governed by the CFAA. If a crawler is used to bypass security measures, such as login requirements or paywalls, it could be considered unauthorized access and lead to criminal charges.
- Legal Precedents: There have been legal cases where companies have sued over unauthorized crawling, arguing that it constituted a breach of contract or unauthorized access. Outcomes of these cases vary, with some courts siding with the website owners and others with the crawlers, depending on the specifics of the case.
6. Ethical Considerations
Transparency: Being transparent about crawling practices and respecting the intentions of website owners (as expressed in robots.txt or terms of service) is a good ethical practice.
Server Load and Bandwidth: Even if crawling is legal, it can be unethical if it places an excessive load on a website’s servers, potentially disrupting the site’s operation. Ethical crawlers use rate limiting and follow good practices to minimize their impact on the sites they crawl.



















