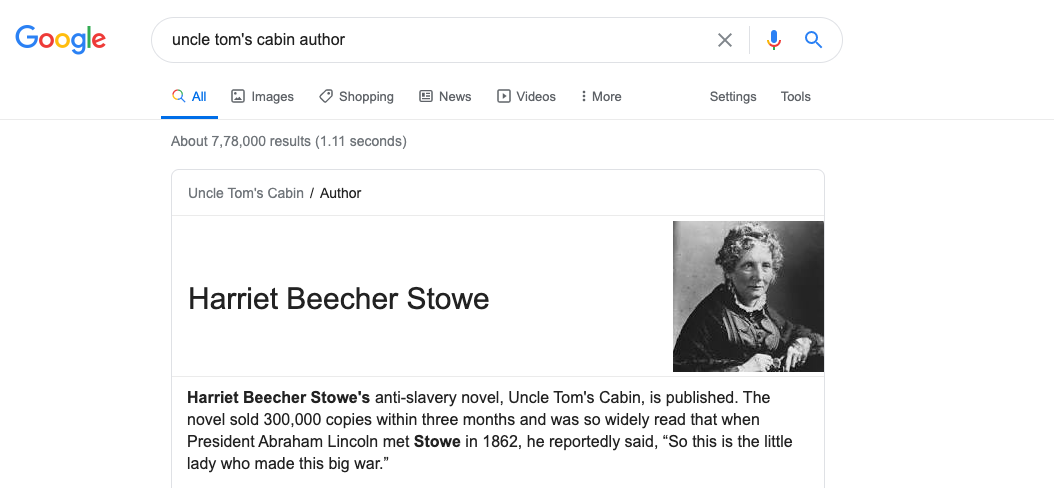
Say you want to know who wrote the book Uncle Tom’s Cabin. You go and type these keywords “Uncle Tom’s Cabin Author” in Google search engine. The keywords do not form a proper statement, but Google can understand what your search query implies. It can relate to the word ‘author’ to Uncle Tom’s Cabin. The result provides you not only the most relevant search results but even a direct answer to the half-baked question and a set of related questions that other people usually ask on related topics. Let us take a look at what semantic search does to your questions on the search engines.
These related questions are the ones that were asked by other users. They also asked different questions on the same topic. It is to be noted that there is a small feedback button at the lower-right corner of the question list. Where you can inform Google whether the questions present there are relevant or completely off the topic.

Such precise search results, from any search engine, would not be possible if search engines directly checked for occurrences of keywords or used weighted occurrences. Instead, search engines use complex algorithms to perform a semantic search. That is, it tries to understand the association between the keywords that you have typed, and understand their meaning, and then search for the best results that match the meaning. For example, if you searched for a well-known personality, Google will use its knowledge graph to present to you the most important or the “most commonly asked-for” bits of information on the person at the very top, so that you can easily find exactly what you are looking for.
What Has Changed over Time?
As per some reports, more than 90% of the web traffic goes through search queries. Even if these numbers decrease with time. A large fraction of internet users will still be using search engines to browse the web. Now all these search queries need to be handled by search engines, of which Google makes up around 86.02 percent as of April 2020. So, we can talk about how Google handles these search queries and how it handled them in the past to discuss how search engines are using semantic search to provide better answers.
The Initial Days Of Semantic Search
The initial search engines worked only if you knew the exact spelling of the website you needed to get into. Search engines started indexing the data inside websites to provide results around 1994. Search engines like Yahoo used to charge commercial websites $300 to get indexed and there was a long wait time to be included. Most of the earlier websites used some specific tricks. For example, weightage was given on the frequency of keywords on a webpage. Points were also given for links to websites with similar or related content. Search terms were sold for advertising and this is a prevalent practice even today.
These old ways of ranking websites were not foolproof. The results did not always match what you asked for. Due to this reason, Google started building the knowledge graph using enormous quantities of data from the web. One, the knowledge graph connects different data points so that when someone types in keywords in a search bar. Two, the words in the query text will be deciphered to find the starting point in the knowledge graph. Three, based on the word associated with the main keyword, the graph will be traversed to fetch you the exact results.
The Semantic Search Algorithm
The year 2013 saw the beginning of a shift in how search queries were processed by Google with the use of the Hummingbird Algorithm. Named after the speed and accuracy of the tiny bird, the algorithm is still in use. It places greater importance on the context and meaning of the search query instead of the individual keywords themselves. It also goes deeper into individual website pages to display the most appropriate content to users. With these changes, website owners and content creators need to focus on the content and language and not just on the placement of specific keywords and links.
The Effect on Content Creation
The way content was created to get websites at the top of search results and increase organic hits has changed tremendously, since the early 1990s. It now presents a level playing ground and genuine content creators will come up on top. Here are some ways for content creators to improve web pages so it gets picked up by the semantic search algorithm.
Focus More On Content And Not Just Keywords:
Due to the new techniques, specific keywords need not match to get picked for a search query. Similar words, synonyms, or even a completely different text that means the same thing will work just as well. However, the content on the topic needs to be more comprehensive and informative to be ranked higher. For example, if you are writing a review of a mobile phone, instead of using the model number multiple times in hopes of ranking higher. You can go into details of every single feature and answer the probable questions that a customer might have before buying it and mention its shortcomings as well. This way, more queries will fetch your article as a search result.
Include Not Just The Same But Also Related Keywords:
Say you are creating fresh content around some keywords that you need organic hits for. You must find related topics and keywords, and provide some information on those as well. The greater the number of related content you have on your webpage. The greater the chance of Google’s graph tree using your website to fill information on multiple topics.
Structured data is the key:
Structured data parsed very well and very easily by search engines. If you have data in tabular format, related to the topic at hand. The data consumed very easily by algorithms and based on the type of data that you have in your tables. They can display different types of user queries. Structured data also adds more context to your webpage and search engines can understand what your page is all about far better.
The Future of Semantic Search
With the advent of AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP). Expected that search engines will only get better at finding the most appropriate articles and webpages on a topic. Scrape away ones that are irrelevant or try to mimic relevant articles. In such a dynamic and changing landscape recommended that you focus on the topic at hand and improve your data and content based on the topic. Instead of trying to understand how the current generation algorithms are ranking web pages.
If you ever want to scrape or extract data from different websites of your choice. Choose PromptCloud which is a fully-managed data scraping service, catering to the big data requirements of enterprises and start-ups alike. If you liked the content please leave us your valuable feedback in the comments section below.




















